
ANALYSIS
Research Question:
How do different content formats (long-form video on YouTube vs. photo-centric posts on Instagram) impact influencer engagement across various categories, and what does this reveal about audience behavior and platform preferences?
LITERATURE REVIEW
The two social media platforms I’m focusing on are Instagram and YouTube, specifically analyzing how static photos and long-form content perform on each. Static photos were the first step in making social media posts feel more human, moving beyond plain text on a screen. Keib explains in the article Picture Perfect: How Photographs Influence Emotion, Attention and Selection in Social Media News Posts (2023) that “images are central to web design and to how organizations identify themselves visually.” This also applies to Instagram profiles, where influencers carefully curate content to connect emotionally with their audience. These emotional ties shape how users experience and engage with content, making personal resonance a driver of interaction.
Video content also continues on this emotional connection by reshaping how people consume media and engage on social platforms. Rugrien highlights in Social Media Trend 2023: Short-form VS. Long-form Video (2023) that YouTube can be seen as the start of video sharing which has since expanded to live streaming, stories, and vertical videos—offering new ways for creators to share experiences, talents, and perspectives. This shift to video has amplified emotional engagement, creating deeper, passion-driven connections between users and content. Keib reinforces this idea, noting that “emotion is regarded as a key determinant that shapes the overall experience of media use and information processing.” As users scroll and explore, they’re naturally drawn to content that resonates with their interests, shaping their engagement and overall experience.
Over time, users tend to engage specifically in content categories that align with their interests, creating a feedback loop where their preferred topics take precedense on their feed. Keib describes this as selective exposure: “the mechanism through which we maintain control over what we are exposed to in the media.” This explains why certain niches gain such strong engagement—users are actively seeking out content that meets their personal motivations or needs. This dynamic also fuels the visibility of influencers in specific spheres, as communities form around shared interests.
This idea ties closely to the rise of micro-influencers. As Wies et al. explains in Less is More: Engagement with the Content of Social Media Influencers, micro-influencers are “credible, self-made online personalities” with niche, enthusiastic followings. Unlike mainstream celebrities, they captivate smaller but highly engaged communities, often specializing in specific topics that attract a loyal audience. For a subpart of my analysis, I want to explore how engagement differs between smaller creators and those with massive followings. This plays into my larger scope analyzing if these niche communities foster stringer interactions than the broader audiences of top influencers? And which platform—Instagram or YouTube—does a better job supporting these communities? These questions will help uncover which forms of content resonate most effectively on each platform.
VISUALIZATIONS
category popularity
To start off my analysis of how different content formats impact certain categories, I first examined the most popular influencer categories on each platform. Using word clouds created in Voyant, these visualizations provide a broad view of category trends and help uncover how certain types of content thrive on one platform versus another. They also gives a little insight on how certain genres connect with their niche audiences and maintain engagement across varied content forms.
Top YouTube Influencer Categories
(hover over words for count)
Top Instagram Influencers Categories
(hover over words for count)
The YouTube Category cloud illustrates the prominent categories and genres tied to top influencers on YouTube in 2022. Music and dance dominate the space, reflecting the platform’s utility for artists sharing videos designed bingeing, streaming, and mass appeal. Animation and games emerge as the next main categories, emphasizing YouTube's strength in catering to niche communities and creators producing in-depth, long-form content. Politics and news ranking high after that showcases how audiences turn to YouTube for comprehensive and opinion-driven coverage. With how the platform is set up, YouTube’s video-centric approach fosters deeper audience engagement through storytelling, explanations, or performances that differ from static photo platforms, such as Instagram. We can see here how YouTube thrives as a hub for creators and users who are seeking depth in their topics, where long-form content enables the platform to expand in emotional content with more depth and information.
The Instagram Category cloud highlights the dominant categories and genres for top Instagram influencers in 2022. Unsurprisingly, entertainment genres are the most prominent, with the movie and cinema industry as the leading niche. This aligns with Instagram's visual and aspirational nature, which caters to actors and actresses sharing behind-the-scenes moments, premieres, or personal stories. Music emerges as another significant category, reflecting artists leveraging the platform for promotions and fan interactions through photo-centric campaigns. Lifestyle, sports, modeling, and shows follow closely, reinforcing the platform's versatility. It's noteworthy how categories like fashion and beauty dominate in the secondary tier. This suggests that Instagram serves as a vital space for influencers showcasing aspirational content, whether through personal branding or consumer-focused promotions. We can see here how the platform's visual nature favors influencers who can capitalize on aesthetic and narrative appeal in a collection of photos.
category engagement
This bar chart compares the average engagement across the top content genres on Instagram and YouTube. It was made with Python on Google Colab. The average engagement was calculated differently for each platform. The Instagram average engagement came with my dataset which looked at things such as likes and comments per profile, while I calculated the YouTube average engagement through likes, comments, and view counts.

The chart highlights Instagram's dominance in engagement for Fashion & Beauty, Entertainment, Lifestyle, Business & Finance, and Food & Cooking categories. For instance, Fashion & Beauty stands out with engagement levels more than four times higher on Instagram than YouTube. This aligns with the word clouds, which show Instagram’s stronghold in visually driven spheres like fashion, beauty, and entertainment. On the other hand, YouTube outperforms in categories like Technology & Science and Gaming, which thrive on long-form, in-depth content that fosters detailed exploration and storytelling.
This reflects how platform-specific content styles shape engagement, with Instagram favoring quick, visually appealing snapshots, while YouTube caters to audiences seeking immersive and detailed experiences.
general follower activity
To understand how much engagement and activity on influencers' profiles come from their followers versus a broader audience interested in the topic, I analyzed engagement trends across all influencers in my dataset with a scatterplot. The scatterplot was made with Python on Google Colab. This visualization maps the relationship between an influencer's follower count and their engagement rate, calculated as in previous analyses. The size of each dot reflects the number of influencers grouped in that similar area.
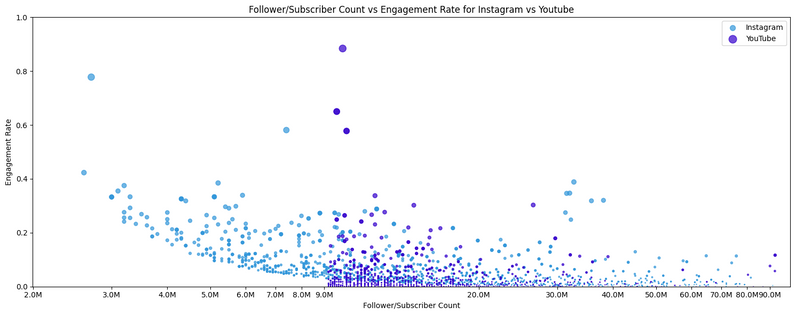
Analyzing the scatterplot shows interesting platform dynamics and trends. One finding is that Instagram’s top influencers have a broad follower range, starting just above 2 million and reaching well over 100 million followers, creating a much wider range of reach compared to engagement. On the other hand, YouTube influencers show a tighter range of subscriber counts, with most top creators having between 9 million and 20 million subscribers (there are a few outliers in this range that go up to past 100 million). Showing that all the top 1000 YouTube influencers have at least 9 million subscribers indicates that there is a higher entry threshold to be a top creator compared to Instagram.
These insights emphasize how each platform shapes influencer growth and audience engagement differently. Instagram supports a wide variety of influencers, from micro to mega-celebrities, allowing for a diverse range of followings. YouTube, in contrast, favors creators with substantial subscriber bases, suggesting that its algorithms and content strategies prioritize creators with significant reach who cater to highly engaged, focused communities. There my be many channels with smaller subscriber counts, but it may be all up to outward interactions that drive views and engagements. This distinction reflects how the platforms cater to varying audience behaviors and engagement models and how possible niches, focused categories on YouTube would not be considered a big channel, even though the engagement rates may be higher.
These findings are complemented by the findings by Wies et al. (2022) which highlights how larger influencers reach broader audiences but still tend to experience lower engagement rates in comparison to their mass follower numbers. They write that “that although influencers with a higher follower count reach a greater audience, their followers are less likely to engage with their content”. When comparing the follower counts and the categories that have higher engagement on specific platforms, this idea holds true. It aligns with the idea that Instagram influence profiles attract followers more for a general visibility and simple life updates, rather than deeper communities and connections.
Now when we look at YouTube, there is room to say that YouTube’s tighter subscriber count range and higher engagement patters reflect how the platform is a more niche, categorical oriented with strong and passionate communities. Even though YouTube also attracts larger audiences in general, there is a more consistent engagement rate across different following amounts.
a detailed look
One way to dive deeper into this comparison is by focusing on the similarities between Instagram and YouTube and seeing how they each perform in comparable situations. A prominent example is the rise of short-form content and how both platforms have incorporated it—through Instagram Reels and YouTube Shorts. Short-form video is defined as content “designed to convey a concise message or capture the viewer’s attention quickly,” often delivered as “bite-sized content with engaging visuals and storytelling” (Rugrien). This format has given creators and influencers a fresh way—aside from each platform’s main content style—to connect with their audience.
To explore this, I analyzed Reels and Shorts for 14 different influencers per platform, selecting 2 influencers per category. While this is a smaller sample size, it provides a closer look at how short-form content is being used in different categories. With this, I can gain deeper insights into how engagement with short-form video varies depending on the platform and the content category.
The bar graphs reveal how Reels and Shorts perform differently across categories. Instagram Reels consistently outperforms Shorts in average likes, comments, and views across categories like Food, Entertainment, and Tech, underscoring the platform's strength in visually-driven, interactive content.
However, Shorts show higher average engagement overall, especially in categories like Lifestyle and Fashion & Beauty, emphasizing YouTube’s focus on niche, dedicated audiences built around long-term content consumption. This contrast highlights how each platform’s functionality and audience behavior influence the reach and depth of creator-audience connections.
These findings are critical for understanding the relationship between content type, platform, and audience interaction. They support my subquestions about how short-form content is received in different categories and whether audience engagement varies based on the platform. By identifying these patterns, my analysis shows on how creators can and potentially optimize their strategies depending on their niche and engagement goals. This gives practical insights into how different content categories are affected by platform-specific trends.



